
QUICK SUMMARY
The summaries below are meant for a psychiatry resident level of training and above (i.e. inappropriate/excessive level of detail for medical student purposes). Please note this page is incomplete. The information below should not replace clinical judgement. Abbreviations are used and levels of evidence are omitted for brevity purposes
DSM-5 / DEFINITIONS
- Late onset schizophrenia = onset 40-60/65 yo
Very-late onset SCZ-like psychosis = onset > 65 vs 60 yo
Late onset bipolar disorder = onset > 50 yo
Late-life depression = onset > 60 yo
Late onset Alzheimer’s = onset > 60 yo - Metabolic syndrome = 3+/5 following: Waist circumference > 102 cm (40″) in men OR 88 cm (35″) in women; BP > 130/85 mmHg; Triglyceride > 1.7 mmol/L (150 mg/dL); HDL < 1 mmol/L (40 mg/dL) in men OR 1.3 mmol/L (50 mg/dL) in women; Fasting glucose > 5.6 mmol/L (100 mg/dL) or abnormal A1C (5.7 to 6.4 percent)
INVESTIGATIONS
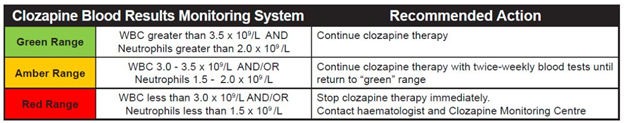
- Additional f/u investigations for clozapine: CBC q wk x 1st 6 mo (12 mo if rechallenging clozapine after moderate leukopenia) –> q 2 wk x next 6 mo –> q 4 wks; vitals 6-8 hrs post-dose for 1st 4 doses of initiation; vitals + S&S myocarditis (fever, fatigue/malaise, chest pain) q2d (if inpt) vs q wk (if outpt) x 1st mo; CRP + troponin q wk x 1st 4 wks, at wk 6, at wk 18, at 6 mo then q 6 mo; ECG at 6 mo then q yr; echo at 6 mo and PRN; baseline nor/clozapine serum level
Mood Disorders
- Baseline investigations for bipolar disorder: History, collateral, physical exam, rating scales (Young Mania Rating Scale, Mood Disorders Questionnaire, mood chart), UDS, CBC, chem panel, calcium, albumin, U/A, +/- 24 hr CrCl (if renal disease), liver panel, TSH, lipid panel, fasting glucose, BMI, +/- ECG (if 40+ / PRN), +/- beta-hCG, +/- PRL, +/- HLA-B*1502 genotyping in Hans Chinese
- F/u investigations for lithium: Li, CBC, chem panel, U/A, calcium, albumin, TSH +/- T3, vitals, BMI, fasting glucose, lipid at 6 month mark (vs q 3 mo x 1 year) then annually (vs q6mo)
- F/u investigations for VPA: CBC, full liver panel, menstrual hx (for PCOS) q 3-6 mo x 1st yr –> q yr; VPA serum levels at therapeutic dose x 2 –> q 3-6 mo
Neurocognitive Disorders
- Baseline investigations for cognitive impairment: History, collateral, physical exam, cognitive testing, functional testing, depression screening, +/- neuropsych testing, +/- UDS, +/- heavy metal, CBC, chem panel, calcium, albumin, +/- PO4, +/- Mg, +/- NH3, U/A, liver function tests, TSH, vitamin B12, +/- folate, fasting glucose or A1C, lipid panel, BP, ESR, +/- HIV, +/- neuroimaging, +/- CSF, +/- genetic testing/counselling
Eating Disorders
- Investigations for eating disorders: History, collateral, rating scales, physical exam (orthostatic vitals, hydration status, height/weight +/- growth chart, sit up-squat-stand test), CBC, ferritin, transferrin, B12, zinc, chem panel, ext lytes, U/A, full liver panel, TSH, T3, T4, lipid panel for AN, ECG, +/- stool exam if GI bleeding/abdo c/o/anemia, amylase if purging. If underweight > 6 mo = abdo u/s, FSH, LH, estradiol or testosterone, DEXA scan.
MANAGEMENT
Major depressive disorder
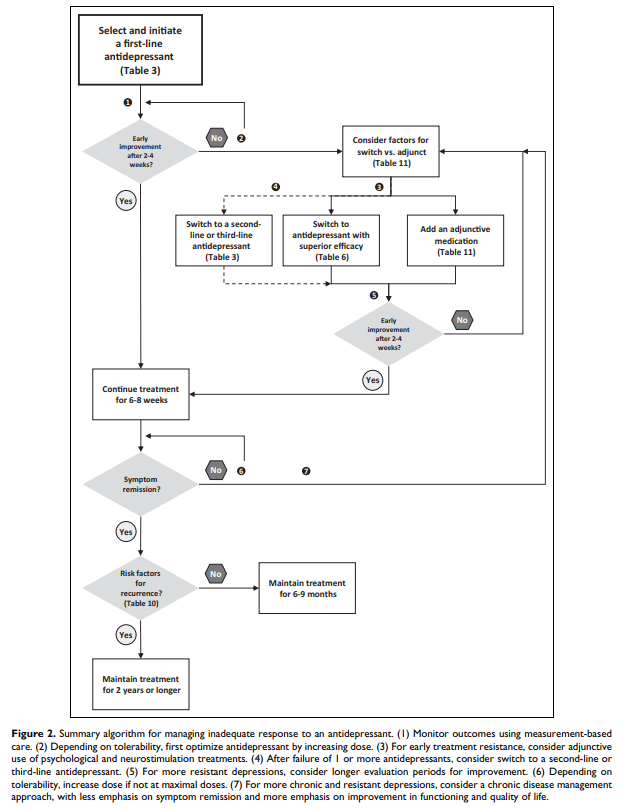
- Early improvement = 20-30% improvement at 2-4 wk mark; Expected onset of full response to ADT for MDD = 6-12 wks
- 1st line meds = all SSRIs, all SNRIs excl levomilnacipran, vortioxetine, bupropion, mirtazapine
- ADT w/ superior efficacy per CANMAT = sertraline, escitalopram, mirtazapine, venlafaxine > citalopram (L2E)
- Best overall tolerability and efficacy = escitalopram, vortioxetine

- 2nd line meds = levomilnacipran, vilazodone, trazodone, quetiapine, TCAs, moclobemide, selegiline
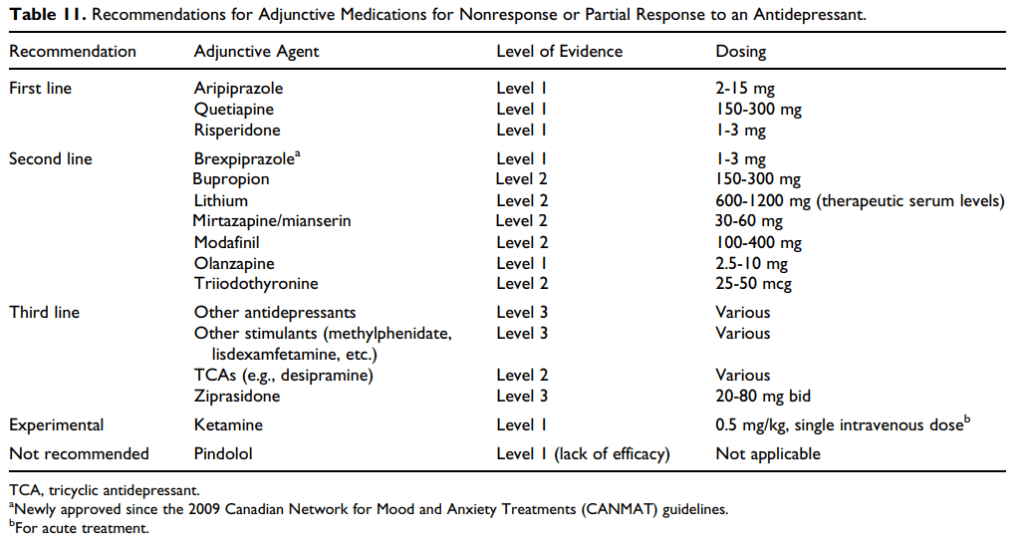
- Psychological tx for MDD
- For maintenance tx: 1st line = CBT, mindfulness-based cognitive therapy; 2nd line = IPT, behavioral activation, cognitive-behavioral analysis system of psychotherapy; 3rd line = long-term psychodynamic; 2nd line adjunct = bibliotherapy, peer interventions (eg self-help groups)
Bipolar disorder
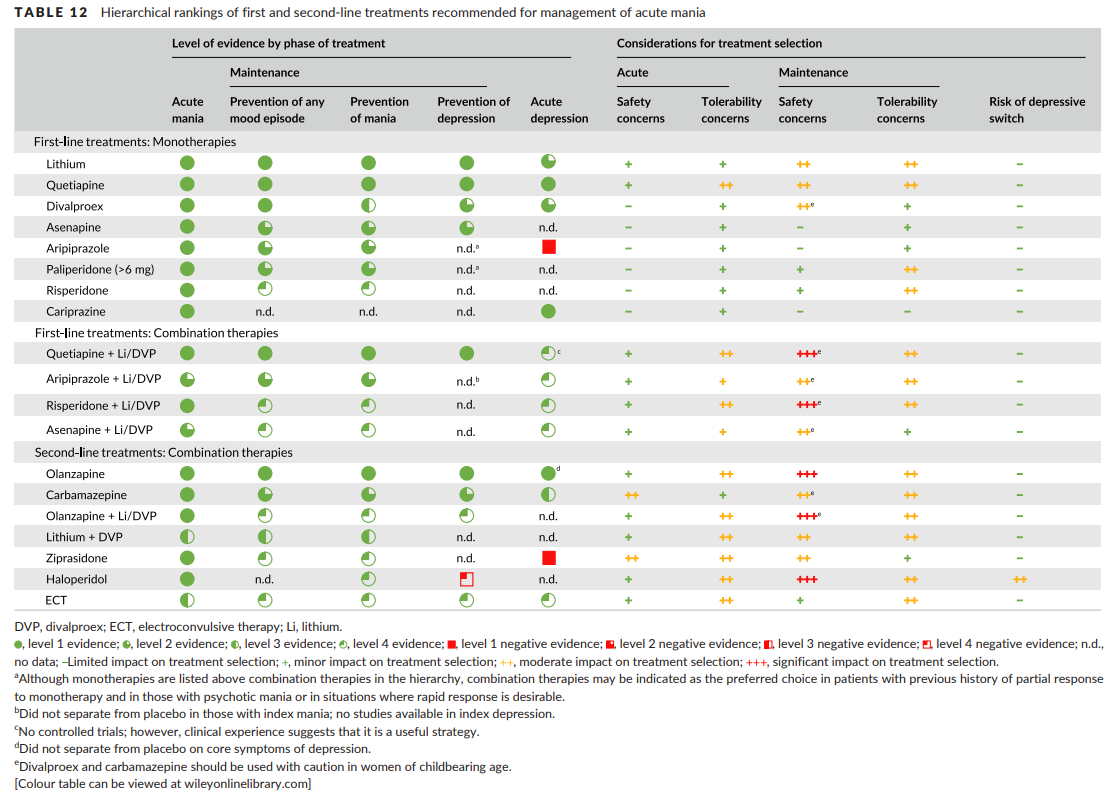
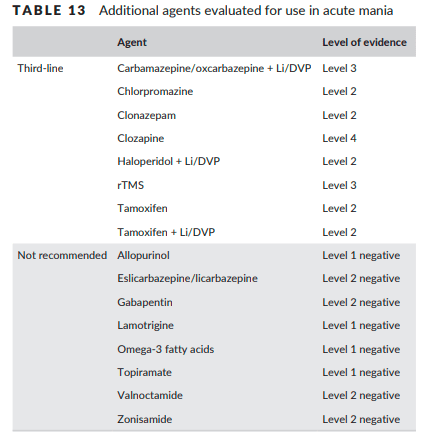

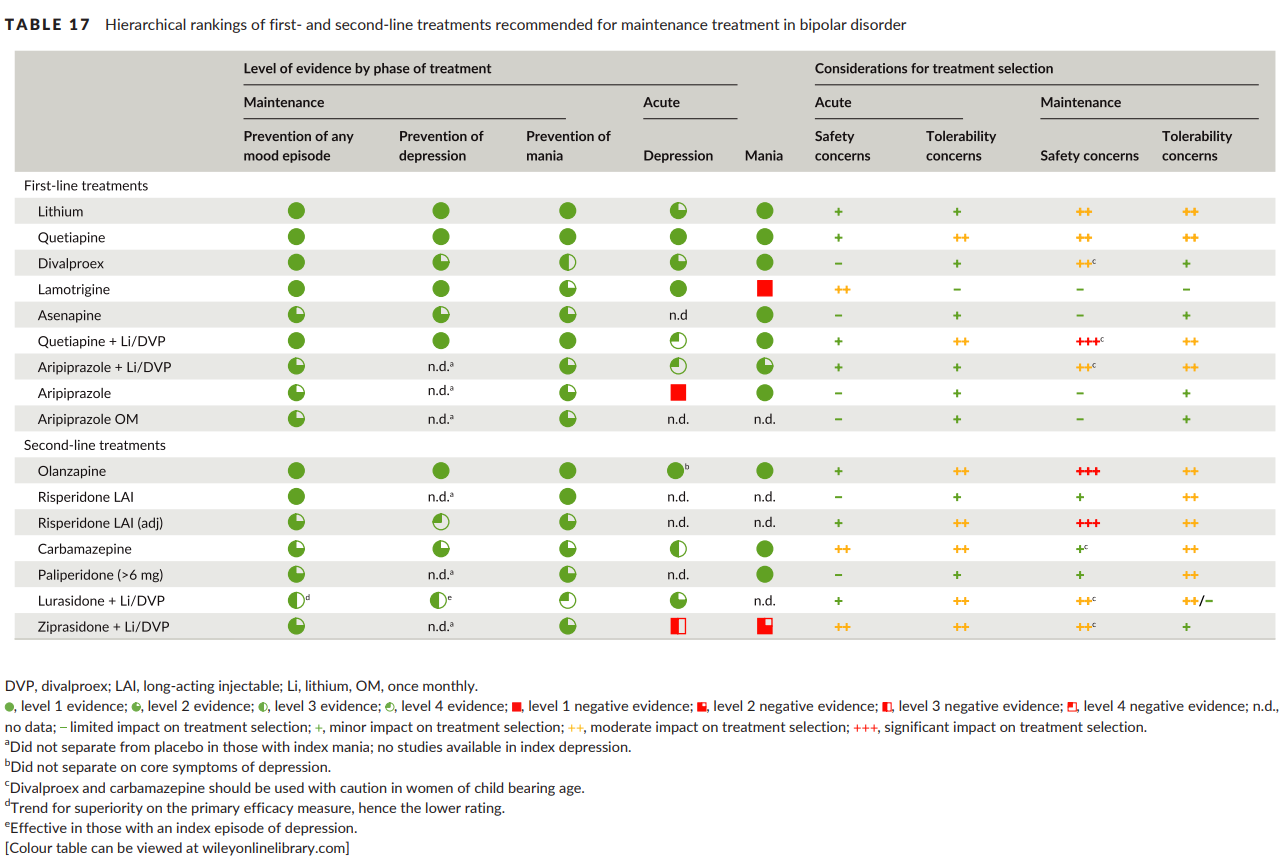
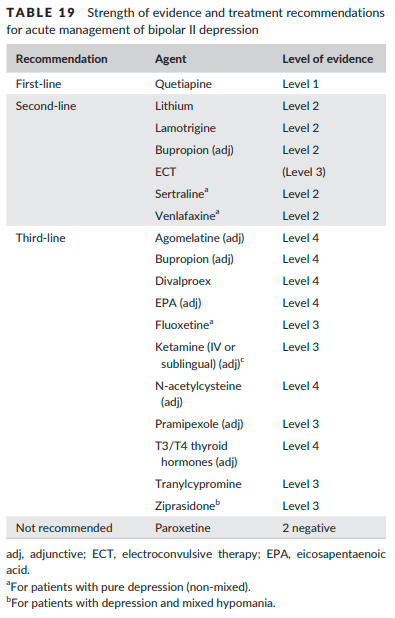
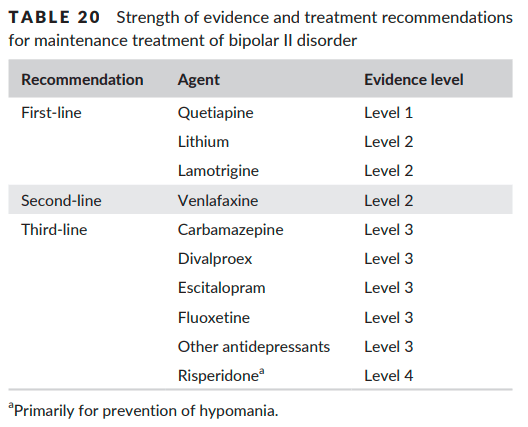
- Takes ~2 weeks for onset of action w/ 1st line agents for BID MDE vs 1-3 weeks for onset of action with Li
- Antidepressant monotherapy not recommended if prior antidepressant-induced hypo/mania, rapid cycling, or mixed features
- Risk factors for manic switch: BID, prior hypo/manic switch, SNRIs and TCAs > SSRI and bupropion
- Rapid cycling
- Discontinuing offending perpetuating factors, most commonly antidepressants (including adjuncts; will require taper, not abrupt discontinuation), psychostimulants, substance use, and hypothyroidism
- There is insufficient evidence to support a particular 1st line agent. Instead, consider medication efficacy in the standard treatment of acute episodes / maintenance treatment. Combination therapy is often required. Lithium, divalproex, olanzapine, and quetiapine have all been equally efficacious for maintenance treatment. Lamotrigine is not effective for maintenance treatment
- Tx of comorbid primary anxiety and related disorder
- 1st line = quetiapine, gabapentin
- 2nd line = serotonergic ADT, olanz-fluox combo, olanz, DVP, lamotrigine
- 3rd line = pregabalin, risperidone, aripiprazole, lithium, medium/long-acting benzo
- Tx of comorbid ADHD (BD should be stable x 3 mo w/ good community supports to monitor before starting psychostimulants. Start low / go slow, closely monitor)
- 1st line = bupropion (in BIID)
- 2nd line = methylphenidate, mixed amphetamine salts, modafanil, CBT
- 3rd line = Vyvanse, atomoxetine, venlafaxine, nortriptyline, desipramine
GAD
- 1st line = paroxetine, escitalopram, sertraline, venlafaxine, duloxetine, pregabalin
- 2nd line = diazepam, lorazepam, alprazolam, bromazepam, buspirone, quetiapine XR, hydroxyzine, imipramine, vortioxetine, bupropion XL
- 2nd line adjunct = pregabalin
- 3rd line adjuncts = quetiapine, risperidone, olanzapine, aripiprazole
Social anxiety disorder
- 1st line = paroxetine, escitalopram, sertraline, fluvoxamine, venlafaxine, pregabalin
- 2nd line = gabapentin, clonazepam, alprazolam, bromazepam, phenelzine
- 3rd line adjuncts = risperidone, aripiprazole, paroxetine, busprione
Agoraphobia / panic disorder
- 1st line = fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, es/citalopram, sertraline, venlafaxine
- 2nd line = mirtazapine, clomipramine, imipramine, clonazepam, diazepam, lorazepam, alprazolam
- 2nd line adjuncts = clonazepam, alprazolam
- 3rd line adjuncts = aripiprazole, olanzapine, risperidone, divalproex, pindolol
- 3rd line = duloxetine, bupropion, moclobemide, phenelzine, tranylcypromine, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, DVP, gabapentin, levetiracetam
PTSD
- No role for benzodiazepines
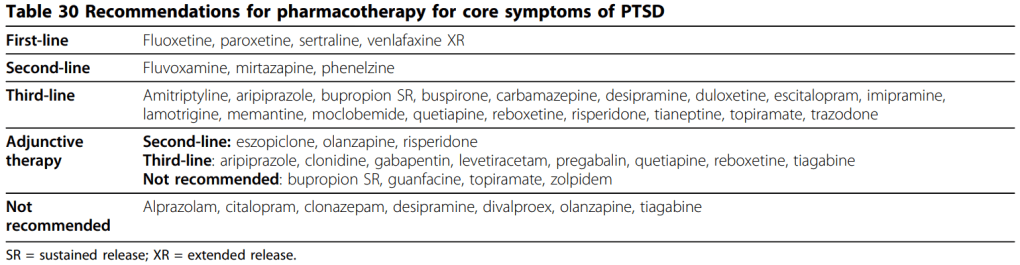
OCD
- 1st line med = all SSRIs except citalopram
- 1st line psychotherapy = CBT including ERP
- 2nd line med = clomipramine > citalopram, mirtazapine, venlafaxine XR
- 1st line adjuncts = risperidone, aripiprazole
- 2nd line adjuncts = quetiapine, memantine, topiramate
ADHD
- 1st line = long-acting psychostimulant
- 2nd line = switch to other class of long-acting psychostimulant
- 3rd line = intermediate/short-acting psychostimulant, atomoxetine, guanfacine XR (not recommended for adult ADHD)
- 4th line = clonidine, bupropion, impramine, atypical antipsychotic for comorbidities (has evidence for hyperactivity in ASD+ADHD), modafanil (no efficacy for adult ADHD)
Subclinical Hypothyroidism
- General consensus to treat w/ L-thyroxine if TSH > 10
- Tx when TSH betw UNL (4-5 in adults; different in geri and pregnancy) and < 10 is controversial
- If TSH 7-9.9 = tx all (only if sx if geri)
- If TSH betw UNL to < 7 = tx < 65 yo only if symptomatic or women trying to conceive (don’t tx > 65 yo)
- Monitor for progression to overt hypoTSH (eg q 3 mo)
Antipsychotic-Induced Hyperprolactinemia
- Repeat fasting PRL if initial PRL 21-40 ng/mL
- Asymptomatic = no tx
- Symptomatic = reduce dose or switch to less offensive AP (aripiprazole, quetiapine, CLZ); aripiprazole adjunct; adjunctive estradiol and progestin to tx estradiol deficiency in women vs adjunctive testosterone to tx testosterone deficiency in men (does not tx the hyperPRL); adjunctive dopamine agonist (eg bromocriptine)
CONSIDERATIONS FOR CHOOSING PSYCH MEDS
Antipsychotics
- Do not rechallenge clozapine (all else can potentially rechallenge given appropriate surveillance/management/prophylaxis) if = myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, QTc > 500, ANC < 500/uL (unless maybe there was confounding factors)
| Relative efficacy for positive psychotic symptoms | EPS | HyperPRL | Metabolic | Sedation | QTc | Breastfeeding Risk | Special Admin | |
| Haloperidol | Med | High | Low | Low | High (esp IV) | Best TAP | ||
| Chlorpromazine | Higher | Med | Med-High | High | High | |||
| Risperidone | *Higher* | Med | Med-High | Low | ||||
| Paliperidone | Higher | Med | Med-High | Low | ||||
| Lurasidone | Lower | High | Low | *Low* | Take w/ food | |||
| Ziprasidone | Med | Med | *Low* | Low | High | Take w/ food, BID | ||
| Olanzapine | Higher | Low | *High* | Med | Best AAP (1st choice) | |||
| Quetiapine | Med | Low | Low | *High* | Med | High | ||
| Asenapine | Med | Low | Low | Low | SL, poor taste (not good if paranoid), BID (OD if overly sedating) | |||
| Clozapine | *Higher* (gold standard for TRS) | Low | Low | *High* | High | Multi SE, bloodwork | ||
| Aripiprazole | Lower | Med (akathisia) | Low | *Low* | Low | *Low* | ||
| Brexpiprazole | Lower | Low | Low | |||||
| Cariprazine | Lower | Low |
Antidepressants
| Evidence for MDD | Evidence for Anxiety and Related D/o | Other Indications | GI Upset | Weight Gain | Sexual Dysfunction | QTc | Peripartum | |
| Escitalopram (Cipralex) | *1st line w/ superior efficacy | *Lowest | Medium | High | ||||
| Citalopram (Celexa) | 1st line | *Highest | High | Last choice SSRI in breastfeeding | ||||
| Sertraline (Zoloft) | *1st line w/ superior efficacy | 1st line PTSD | *Highest | Best if AT RISK | 1st choice SSRI in breastfeeding | |||
| Fluoxetine (Prozac) | 1st line | 1st line PTSD | *Highest | High | Last choice SSRI in breastfeeding | |||
| Paroxetine (Paxil) | 1st line | 1st line PTSD | High | *Highest | High | |||
| Fluvoxamine (Luvox) | 1st line | 2nd line PTSD | *Highest | High | ||||
| Venlafaxine (Effexor) | *1st line w/ superior efficacy | 1st line PTSD | Neuropathic pain | *Highest | High | |||
| Desvenlafaxine (Pristiq) | 1st line | Neuropathic pain | Low | |||||
| Duloxetine (Cymbalta) | 1st line | Neuropathic pain | *Highest | Best if already prolonged | ||||
| Levomilnacipran (Fetzima) | Neuropathic pain | *Lowest | Medium | |||||
| Bupropion (Wellbutrin, Zyban) | 1st line | 3rd line agent for ADHD | *Lowest | *Lowest | Best if already prolonged | |||
| Mirtazapine (Remeron) | *1st line w/ superior efficacy | 2nd line PTSD | – Akathisia – Sleep (lower doses) | *Lowest | *Highest | *Lowest | ||
| Vortioxetine (Trintellix, Brintellix) | *1st line w/ superior efficacy | *Lowest | High | Best if already prolonged | ||||
| Vilazodone (Viibryd) | *Lowest | *Lowest | ||||||
| Most TCAs | – Neuropathic pain – Sleep – Imipramine 3rd line agent for ADHD | High (most TCAs) | High (most TCAs) | Ideally avoid doxepin in breastfeeding | ||||
| Moclobemide | *Lowest | |||||||
| Phenelzine | 2nd line PTSD | |||||||
| Trazodone | Sleep |
Benzodiazepines
- Longest half-life = flurazepam > diazepam
- Shortest half-life = midazolam > alprazolam
- Safest in liver dysfunction = “LOT” (lorazepam, oxazepam, temazepam); other benzos are contraindicated
Substance Use Adjuncts
- Contraindications for naltrexone = severe liver disease (Child-Pugh Score C, ALT and AST > 3x UNL), recent opioid use (within 5 days for short-acting vs 7 days for long-acting); caution with mild hepatic dysfunction and mod-severe kidney dysfunction
- Contraindications for acamprosate = severe renal dysfunction (ie GFR < 30; caution if mild-mod), adherence issues; caution if pregnancy, breastfeeding or < 60 kg
- If prolonged QTc = naltrexone, gabapentin not classified. No info re disulfiram or acamprosate.
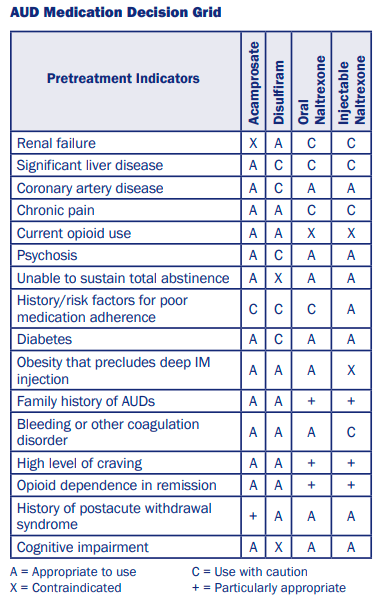
PSYCH MED DOSING IN HEALTHY ADULTS
- Stahl, S.M. (2020). Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology Prescriber’s Guide, 7th edition. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. (Good for referencing specific dosing/information on specific psychiatric medications; not good as an introduction for psychiatric medications.)
- UptoDate / Lexicomp Drug Monograph
- www.switchrx.com (Good for guidance on specific dosing when switching meds; to supplement Stahl’s)
- SMI Advisor for PO and LAI antipsychotic drug conversion
- CPNP Antipsychotic Dose equivalents
- Study Buffalo Drug Price Calculator (Good for comparing drug prices under different coverages in Alberta)
- Dalhousie Psychotropic Medication Dosing Yellow Card
Atypical Antipsychotics for psychotic/bipolar disorders
- Average time to reach steady state for most LAI = 8-12 weeks
- Aripiprazole (lowest dose ever seen is 150 mg (not effective) vs 200 mg; lowest frequency ever seen is q14d; 350 mg is possible w/ 400 mg syringe)
| Aripiprazole PO | Abilify Maintena q4wks +/- 1 week |
| 10 mg | 300 mg |
| 15 mg | 400 mg |
| 20+ mg | 600 mg (not practically used) |
- Risperidone / paliperidone
- Risperidone PO for psychosis/mania = start at 1 (to 3) mg/day in 1-2 divided doses –> increase by 1-2 mg/day as fast as q 24 hr (but try to assess for full effect for > 1 wk vs few weeks) –> target dose 2-8 mg (max 8 mg (clinically recommended max dose) vs 16 mg (per manufacturer’s labelling))
- Invega Sustenna (lowest frequency ever seen is q 2 weeks)
- Invega Trinza (lowest frequency ever seen is q 8 weeks, equivalent to Sustenna q 3 weeks)
- Prerequisite = stable on Sustenna x 4 mo + last 2 doses consistent
| Risperidone PO | Risperidone Consta q2wks | Paliperidone PO | Invega Sustenna q4wks +/- 1 wk | Invega Trinza q12wks +/- 2 wks |
| 1 mg | 12.5 mg | < 3 mg | – | – |
| 2 mg | 25 mg | 3 mg | 50 mg | 175 mg |
| 3 mg | (25 to) 37.5 mg | 6 mg | 75 mg | 263 mg |
| 4 mg | (37.5 to) 50 mg | 9 mg | 100 mg | 350 mg |
| 5 mg | 37.5-50 mg | – | – | – |
| 6 mg | 50 mg | 12 mg | 150 mg | 525 mg |
- Quetiapine
- For psychosis = start at 100 mg –> increase by 100 mg daily to target 600 mg (max 800 mg)
- Lurasidone
- For BID MDE = start at 20 mg PO OD in evening w/ 350+ calories (can take initially w/out food for ease of side effects) –> increase by 20 mg q 2+ days to target 20-60 mg (max 120 mg/d)
- Clozapine
- Minimum for clozapine-refractory SCZ = 1100 nM/L (350 ng/mL)
Maximum = 2100 nM/L (700 ng/mL)
Seizure-inducing = 3600 nM/L (1200 ng/dL) - nM/L = Canadian measurement
ug/L (microgram/L) = ng/mL (Cortisol conversion to nmol/L, µg/L, µg/dL, µg/100mL, µg%, ng/mL . Online converter from conventional units to SI units | UNITSLAB.COM)
- Minimum for clozapine-refractory SCZ = 1100 nM/L (350 ng/mL)
Mood Stabilizers
- Lamotrigine = typical max 200 mg/d (some literature for max 400 mg/d)
Antidepressants and Adjunctive Antipsychotics for Depression/Anxiety
| Med | Starting Dose | Smallest Formulation in Canada | Titrate Schedule | Target Dose (per 2023 CANMAT MDD guidelines) | Max Dose |
| Escitalopram (aka Cipralex) | 10 mg PO OD for MDD vs 5-10 mg PO OD for GAD | 10 mg tablet | 5-10 mg/d q 1+ wk | 10-20 mg PO OD for MDD | Usually 20 mg PO OD for MDD vs 40 mg PO OD for OCD |
| Citalopram (aka Celexa) | 10 mg PO OD for GAD vs 20 mg PO OD for MDD | 10 mg/d q week (q 3-4 d if inpt) | 40 mg PO OD (20 mg/day if > 60 yo) | ||
| Sertraline (aka Zoloft) | 50 mg PO OD for MDD | 25 mg capsule | 25-50 mg PO OD q 1 week for MDD (q3d w/ antipsychotic if psychotic features) | 50-200 mg PO OD for MDD | 300 mg PO OD |
| Fluvoxamine (aka Luvox) | 50 mg PO OD for MDD | 50 mg tablet | 100-300 mg/d in BID dosing for MDD | 300 mg/d in BID dosing | |
| Paroxetine (aka Paxil) IR | 10-20 mg PO OD for anxiety vs 20 mg PO OD for MDD | 10 mg IR tablet | 10 mg/d q 1 week for anxiety vs 10-20 mg/d q 1 week for MDD | 20-50 mg PO IR OD for MDD | 50 mg PO OD for MDD vs 60 mg PO OD for anxiety |
| Paroxetine (aka Paxil) CR | 12.5-25 mg PO OD for anxiety vs 25 mg PO OD for MDD | 12.5 mg CR tablet | 12.5 mg/d q 1+ week | 62.5 mg PO OD for MDD vs 75 mg PO OD for anxety | |
| Vortioxetine (aka Trintellix) | 5-10 mg PO OD | 5 mg tablet | 5-10 mg/d q 1 wk | 10-20 mg PO OD for MDD | 20 mg PO OD |
| Vilazodone (aka Viibryd) | 10 mg PO OD | 10 mg tablet | Increase to 20 mg PO OD after 7 days then increase to 40 mg after 7+ days if needed | 20-40 mg PO OD | 40 mg PO OD |
| Desvenlafaxine ER (aka Pristiq) | 50 mg PO OD for MDD | 50 mg ER tablet | Increase to 100 mg PO OD after 6 weeks if no response | 50-100 mg PO OD for MDD | 100 mg PO OD |
| Duloxetine (aka Cymbalta) | 30 or 60 mg PO OD for MDD/GAD/pain | 30 mg DR capsule | 30 mg PO OD x 1 wk then 60 mg PO OD x 4-6 wks then 90 mg x 3+ wks then 120 mg PO OD (vs q 3-4d if inpt) | 60-120 mg PO OD for MDD/GAD/pain (usually sufficient at 60 mg PO OD) | 120 mg PO OD |
| Levomilnacipran ER (aka Fetzima) | 20 mg PO OD for MDD | 20 mg ER capsule | Increase to 40 mg PO OD on day 3 then by 40 mg PO OD q 2+ days | 40-120 mg PO OD for MDD | 120 mg PO OD |
| Mirtazapine (aka Remeron) | 15 mg PO qhs for MDD | 15 mg tablet | 15 mg/d q 1+ week for MDD | 30-60 mg qhs for MDD | 60 mg PO qhs |
| Bupropion (aka Wellbutrin, Zyban) | 150 mg 24 hr XL tablet 100 mg 12 hr SR tablet | 150-450 mg PO OD as primary agent or adjunct for MDD (daily doses above 300 mg should be given in divded doses) | 450 mg PO OD | ||
| Amitriptyline (aka Elavil) | 25-50 mg PO QHS (or in divided doses; 50-100 mg/d if inpt) for MDD | 25-50 mg/d q 1 wk (or q few days if inpt) for MDD | 75-300 mg/d for MDD | ||
| Clomipramine (aka Anafranil) | 25 mg PO OD for OCD | 10 mg tablet | Increase to ~100 mg/d in divided doses over the first 2 weeks then increase after 2-3 week PRN for OCD vs 50 mg PO OD q2-3d for MDD | 150-300 mg/d in divided doses for MDD | 300 mg/d in divided doses |
| Doxepin | 25-50 mg PO qhs | 3 mg tablet 10 mg capsule | 25-50 mg/d q 3+ days | 75-300 mg PO QHS for MDD | |
| Aripiprazole (aka Abilify) adjunct for depression/anxiety | 2-5 mg PO OD for MDD | 2 mg tablet | 5 mg/d q 1-2 weeks | 2-10 mg PO OD for MDD | 15-20 mg/d for MDD vs 30 mg/d for psychosis |
| Brexpiprazole (aka Rexulti) adjunct for MDD | 0.5-1 mg PO OD | 0.25 mg tablet | As fast as 1 mg/d q week | 0.5-2 mg PO OD for MDD | 3 mg PO OD for MDD vs 4 mg PO OD for SCZ |
| Cariprazine (aka Vraylar) adjunct for MDD | 1.5 mg PO OD for MDD | 1.5 mg capsule | Increase to 3 mg PO OD on day 15 | 1.5-3 mg PO OD for MDD | 4.5 mg PO OD for MDD |
| Quetiapine (aka Seroquel) | 50 mg PO QHS for MDD | 150-300 mg PO qhs as primary agent or XR as adjunct for MDD |
Benzodiazepines
- Lorazepam 1 mg = diazepam 5 mg = clonazepam 0.25 (to 0.5) mg = alprazolam 0.5 (to 1) mg
Cognitive Enhancers
- Donepezil = start at 5 mg PO qAM –> increase in 4 weeks to target dose of 5-10 mg PO OD
- Memantine = start at 5 mg PO OD –> increase by 5 mg/day q week (ie week 2 = 5 mg BID; week 3 = 10 mg qAM + 5 mg qhs) to max 10 mg BID
SUD Adjuncts
- Naltrexone
- For AUD = +/- start at 25 mg PO OD x several days –> target 50 mg PO OD to max 100 mg PO OD after 1 week
- Gabapentin (for AUD) = start at 300 mg PO OD –> increase by 300 mg q1-2d to effect or target dose 600 mg TID
Other
- Benztropine
- For PRN acute treatment of EPS = 0.5-*2* PO/IM/IV TID PRN EPS, max 8 mg/24 hrs all sources, can repeat initial dosing (ie max 4 mg single dose) if no improvement in 20-30 min
- Scheduled = start at 1 mg OD (0.5 mg for Parkinsonism; range from 0.5-4 mg OD or BID) –> increase by 0.5-1 mg q 5 days to target dose 2-8 mg/day in 1-3 divided doses (0.5-6 mg/day for Parkinsonism) –> attempt taper after 7-14 days to several months to see if EPS transient/resolved (otherwise intermittently trial discontinuation)
- Metformin = start at metformin ER/IR 500 mg OD (or metformin IR 250 BID or 500 mg BID) –> increase by 500 mg/d q 2-6 week for ER vs q 7 day (5-30 days) for IR –> target 1000-2000 mg OD for ER vs 750-2000 mg/day in 2-3 divided doses for IR (ER version not covered by AB Blue Cross)
- L-thyroxine = start at 0.025 mg/d –> recheck thyroid function tests after 6 wk –> titrate by 0.025 mg q 3-6 wk until TSH normalizes
PSYCH MED DOSE ADJUSTMENTS IN RENAL DISEASE
- As a general rule of thumb, start at the lowest recommended starting dose
- Can use Cockcroft-Gault equation to calculate CrCl more specifically than default lab eGFR
Atypical Antipsychotics
- No adjustments needed = haloperidol (but use w/ caution in dialysis), loxapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, aripiprazole
- Paliperidone = All forms contraindicated if CrCl < 10 mL/min or on any type of dialysis. All LAI forms contraindicated if CrCl 10 to <50 mL/min but can use modified PO dose (start at 1.5 mg PO OD to max 3 mg PO OD). If CrCl 50 to <80 mL/min, dose adjustment required for PO (start at 3 mg PO OD to max 6 mg PO OD), 1 mo LAI (loading dose 100 mg + 75 mg IM on day 1+7 in deltoid, then 50 mg IM q mo in gluteal/deltoid to max 100 mg IM q mo), and 3 mo LAI (limited data). No dosage adjustment required if CrCl > 80 mL/min (but 6 mo LAI contraindicated if CrCl < 90 mL/min).
- Risperidone
- Lurasidone
Mood Stabilizers
- Lithium
- Valproate = No dosage adjustment required if CrCl > 10 mL/min.
- Gabapentin
- Pregabalin
- Topiramate
Antidepressants
- No adjustments needed = citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, (paroxetine)
- Escitalopram = start at 10 mg/d if eGFR < 30 or on dialysis
- Sertraline = start at 50 mg/d if eGFR 15-30 vs start at 25 mg/d if eGFR < 15 or on dialysis
- Venlafaxine = target dose 37.5-112.5 mg/d if eGFR < 30 or on dialysis
- Desvenlafaxine = start at 50 mg q2d if eGFR 30-60 vs max 50 mg q2d if eGFR < 30 or on dialysis
- Duloxetine = start at 30 mg/d if eGFR < 30 or on dialysis
- Bupropion = max 150 mg/d if eGFR < 60 or on dialysis
- Mirtazapine = target 15 mg/d if eGFR < 30 or on dialysis
Benzodiazepines
- Benzos w/ inactive metabolites (ie LOT) preferred
- No adjustments needed = most benzos (including lorazepam and clonazepam) but use w/ caution (monitor for propylene glycol toxicity via osmol gap if using repeated/prolonged/high doses of parenteral lorazepam)
- Chlordiazepoxide = 50% target dose in severe renal insufficiency
Cognitive Enhancers
- No adjustments needed = donepezil, rivastigmine
- Galantamine = caution in moderate renal insufficiency; contraindicated in severe renal insufficiency
- Memantine = target dose 5 mg BID if eGFR 15-30; contraindicated if eGFR < 15
PROLONGED QTc
- Definition prolonged QTc (no consensus on definition)
- Most conservative (per American College of Cardiology) = > 460 (prepubertal), > 470 (postpubertal men), > 480 (postpubertal women)
- Per SCZ guidelines and many psychiatric papers= > 450 (men), > 460 (women)
- Most aggressive = > 440 (male), 460 (female)
- To manually calculate QTc:
- Measure QT interval (start of QRS to end T wave) in lead II or V5-6
- 1 small box = 40 ms; big box = 200 ms
- QTc formula
- If HR 60 = use absolute QT interval
- If HR 60-100 = Bazett formula (QT / RR interval; RR interval = 60/HR; default machine calculation)
- If HR outside 60-100 = Framingham or Fridericia formula
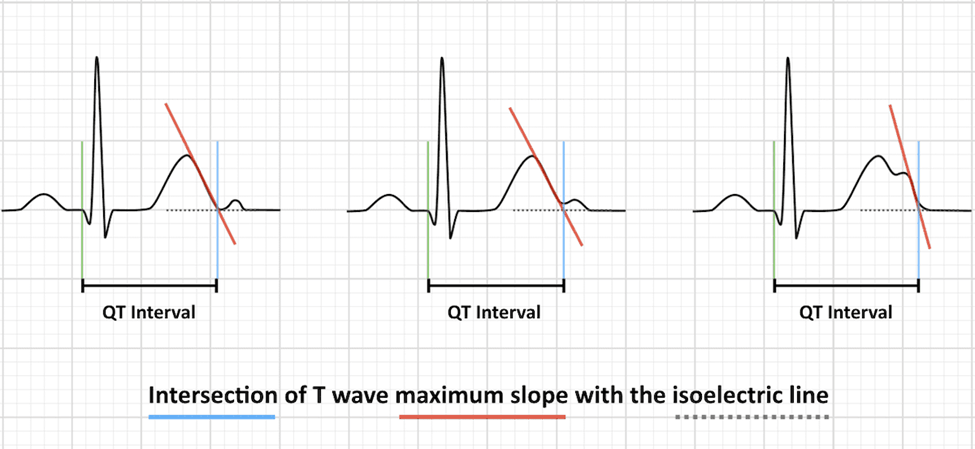
- Risk factors for TdP
- Older age, female
- Prolonged QTc (best predictor) > 500 ms, congenital long QTS
- Multiple drugs that prolong QT interval (esp those metabolized by CYP3A4), drugs that inhibit metabolism of QT-prolonging drug (eg CYP3A4 inhibitors eg grapefruit)
- Previous cardiac adverse effect w/ drugs
- Other pre-existing heart disease (widened QRS eg Brugada syndrome, syncope, low ejection fraction)
- Familial long QT syndrome, family history of sudden death
- Renal disease (electrolyte imbalances, esp hypoK, hypoMg > hypoCa), hepatic disease
- Anorexia nervosa, chronic heavy EtOH use
- Pharmacological management of agitation in psychotic patients with prolonged QTc
- Aripiprazole (only AP safe with QTc > 500 ms) > olanzapine, risperidone, quetiapine > asenapine
- Non-AP (eg if targeting sedation > psychosis tx) = short-acting benzos, trazodone, valproate (not typically used in acute emergencies)
- Recheck BP + ECG throughout
- D/c offending meds if QTc > 500, > 60 ms from baseline, or 25% increase from baseline (consult cardiology)
AGITATION DOSING IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS
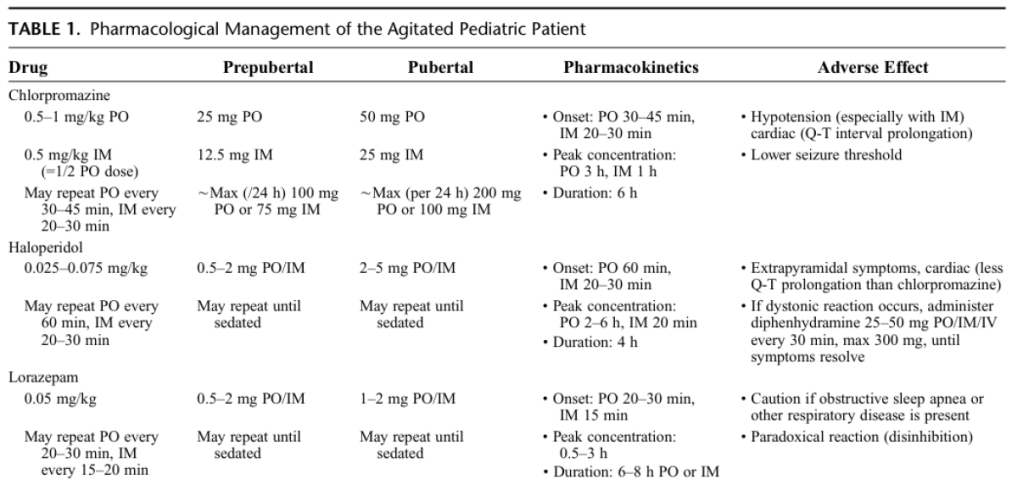
ABBREVIATIONS
- ADT = antidepressant
- Benzo = benzodiazepine
- BD = bipolar disorder
- BID = bipolar I disorder
- BIID = bipolar II disorder
- Fluox = fluoxetine
- DVP = divalproex
- Li = lithium
- LOT = lorazepam, oxazepam, temazepam
- MDD = major depressive disorder
- MDE = major depressive disorder
- Olanz = olanzapine
REFERENCES